Java8 新特性之流式数据处理 #
一:流式处理简介 #
在我接触到java8流式处理的时候,我的第一感觉是流式处理让集合操作变得简洁了许多,通常我们需要多行代码才能完成的操作,借助于流式处理可以在一行中实现。比如我们希望对一个包含整数的集合中筛选出所有的偶数,并将其封装成为一个新的List返回,那么在java8之前,我们需要通过如下代码实现:
List<Integer> numS = Lists.newArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
numS.add(Zhou_StdRandom.uniform(1, 674));
}
List<Integer> evens = new ArrayList<>();
for (final Integer num : numS) {
if (num % 2 == 0) {
evens.add(num);
}
}
evens.stream().sorted().filter(integer -> true).forEach(integer -> System.out.println(integer));
通过java8的流式处理,我们可以将代码简化为:
List<Integer> evens = numS.stream().filter(integer -> integer % 2 == 0).collect(Collectors.toList());
先简单解释一下上面这行语句的含义,stream()操作将集合转换成一个流,filter()执行我们自定义的筛选处理,这里是通过lambda表达式筛选出所有偶数,最后我们通过collect()对结果进行封装处理,并通过Collectors.toList()指定其封装成为一个List集合返回。
由上面的例子可以看出,java8的流式处理极大的简化了对于集合的操作,实际上不光是集合,包括数组、文件等,只要是可以转换成流,我们都可以借助流式处理,类似于我们写SQL语句一样对其进行操作。java8通过内部迭代来实现对流的处理,一个流式处理可以分为三个部分:转换成流、中间操作、终端操作。如下图:
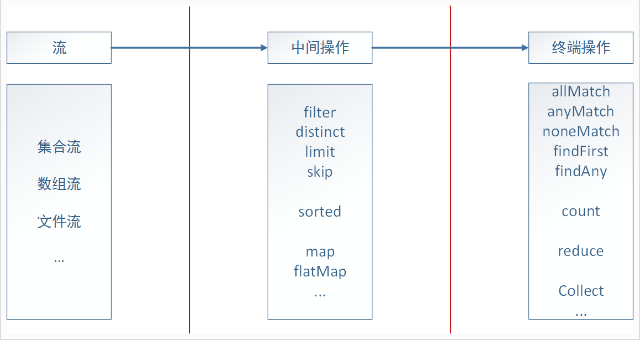

以集合为例,一个流式处理的操作我们首先需要调用stream()函数将其转换成流,然后再调用相应的中间操作达到我们需要对集合进行的操作,比如筛选、转换等,最后通过终端操作对前面的结果进行封装,返回我们需要的形式。
二:创建 #
- 流的创建有多种方式
- 从 Collection 和数组
- Collection.stream()
- Collection.parallelStream()
- Arrays.stream(T array) or Stream.of()
- 从 BufferedReader
- java.io.BufferedReader.lines()
- 静态工厂
- java.util.stream.IntStream.range()
- java.nio.file.Files.walk()
- 自己构建
- java.util.Spliterator
- 其它
- Random.ints()
- BitSet.stream()
- Pattern.splitAsStream(java.lang.CharSequence)
- JarFile.stream()
三:中间操作 #
- 2.1 (过滤,顾名思义就是按照给定的要求对集合进行筛选满足条件的元素,java8提供的筛选操作包括:filter、distinct、limit、skip。)
filter
在前面的例子中我们已经演示了如何使用filter,其定义为:Stream
filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate),filter接受一个谓词Predicate,我们可以通过这个谓词定义筛选条件,在介绍lambda表达式时我们介绍过Predicate是一个函数式接口,其包含一个test(T t)方法,该方法返回boolean。现在我们希望从集合students中筛选出所有武汉大学的学生,那么我们可以通过filter来实现,并将筛选操作作为参数传递给filter:
List<Student> whuStudents = students.parallelStream().sorted().filter(student -> "武汉大学".equals(student.getSchool())).collect(Collectors.toList());
whuStudents.parallelStream().forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
distinct
distinct操作类似于我们在写SQL语句时,添加的DISTINCT关键字,用于去重处理,distinct基于Object.equals(Object)实现,回到最开始的例子,假设我们希望筛选出所有不重复的偶数,那么可以添加distinct操作:
List<Integer> numS = Lists.newArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
numS.add(Zhou_StdRandom.uniform(1, 24));
}
List<Integer> evens = numS.parallelStream().sorted().filter(integer -> integer%2==0).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(evens);
limit
limit操作也类似于SQL语句中的LIMIT关键字,不过相对功能较弱,limit返回包含前n个元素的流,当集合大小小于n时,则返回实际长度,比如下面的例子返回前两个专业为土木工程专业的学生:
List<Student> civilStudents = students.parallelStream().sorted().filter(student -> "土木工程".equals(student.getMajor())).limit(2).collect(Collectors.toList());
civilStudents.parallelStream().forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
skip
skip操作与limit操作相反,如同其字面意思一样,是跳过前n个元素,比如我们希望找出排序在2之后的土木工程专业的学生,那么可以实现为:
List<Student> civilStudents = students.parallelStream().sorted().filter(student -> "土木工程".equals(student.getMajor())).skip(2).collect(Collectors.toList());
civilStudents.parallelStream().forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
- 2.2 (在SQL中,借助SELECT关键字后面添加需要的字段名称,可以仅输出我们需要的字段数据,而流式处理的映射操作也是实现这一目的,在java8的流式处理中,主要包含两类映射操作:map和flatMap。)
map
举例说明,假设我们希望筛选出所有专业为计算机科学的学生姓名,那么我们可以在filter筛选的基础之上,通过map将学生实体映射成为学生姓名字符串,具体实现如下:
List<String> names = students.parallelStream().sorted().filter(student -> "计算机科学".equals(student.getMajor())).map(student -> student.getName()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(names);
flatMap
flatMap与map的区别在于 flatMap是将一个流中的每个值都转成一个个流,然后再将这些流扁平化成为一个流 。
String[] strs = {"java8", "is", "easy", "to", "use"};
List<String> distinctStrs = Arrays.stream(strs)
.map(s -> s.split("")).flatMap(strings -> Arrays.stream(strings))// 映射成为Stream<String[]>
.distinct().collect(Collectors.toList()); // 扁平化为Stream<String>
System.out.println(distinctStrs);
四:终端操作 #
allMatch
allMatch用于检测是否全部都满足指定的参数行为,如果全部满足则返回true,例如我们希望检测是否所有的学生都已满18周岁,那么可以实现为
boolean isAdult = students.parallelStream().allMatch(student -> student.getAge() >= 18);
System.out.println(isAdult?"是":"否");
anyMatch
anyMatch则是检测是否存在一个或多个满足指定的参数行为,如果满足则返回true,例如我们希望检测是否有来自武汉大学的学生,那么可以实现为:
boolean hasWhu = students.parallelStream().anyMatch(student -> "武汉大学".equals(student.getSchool()));
System.out.println(hasWhu?"是":"否");
noneMathch
noneMatch用于检测是否不存在满足指定行为的元素,如果不存在则返回true,例如我们希望检测是否不存在专业为计算机科学的学生,可以实现如下:
boolean noneCs = students.parallelStream().noneMatch(student -> "计算机科学".equals(student.getMajor()));
System.out.println(noneCs?"是":"否");
findFirst
findFirst用于返回满足条件的第一个元素,比如我们希望选出专业为土木工程的排在第一个学生,那么可以实现如下:
Optional<Student> optStu = students.stream().filter(student -> "土木工程".equals(student.getMajor())).findFirst();
System.out.println(optStu.get());
五:常见的操作可以归类如下 #
Intermediate(中间)
map (mapToInt, flatMap 等)、 filter、 distinct、 sorted、 peek、 limit、 skip、 parallel、 sequential、 unordered
Terminal(终端)
forEach、 forEachOrdered、 toArray、 reduce、 collect、 min、 max、 count、 anyMatch、 allMatch、 noneMatch、 findFirst、 findAny、 iterator
Short-circuiting(截取)
anyMatch、 allMatch、 noneMatch、 findFirst、 findAny、 limit
六转换 #
- list 转 Map <key,list>
package com.tool.stream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Demo1 {
public static class TestEntity {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public TestEntity(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public TestEntity() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "TestEntity{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<TestEntity> entityList = new ArrayList<>(2) ;
entityList.add(new TestEntity(1,"图书馆"));
entityList.add(new TestEntity(2,"艺术馆"));
entityList.add(new TestEntity(1,"游泳池"));
// Map<Integer, TestEntity> entityMap = entityList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(TestEntity::getId, user -> user));
//下面的可以确保 百分之百 在key重复下不报错
Map<Integer, TestEntity> entityMap = entityList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(TestEntity::getId, Function.identity(), (oldValue, newValue) -> newValue));
// Map<Integer, String> stringMap = entityList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(TestEntity::getId, user -> user.getName()));
Map<Integer, String> stringMap = entityList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(TestEntity::getId, t -> t.getName(), (oldValue, newValue) -> newValue));
Map<Integer, List<TestEntity>> integerListMap = entityList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(oo -> oo.getId()));
System.out.println(entityMap.get(1));
System.out.println(stringMap.get(1));
System.out.println(integerListMap.get(1));
/*
TestEntity{id=1, name='游泳池'}
游泳池
[TestEntity{id=1, name='图书馆'}, TestEntity{id=1, name='游泳池'}]
* */
}
}
- list 分组统计
package com.tool.stream;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Demo2 {
public static class TestEntity {
private String uuid;
private Double price;
private String name;
public String toString() {
return "TestEntity{" +
"uuid='" + uuid + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public TestEntity(String uuid, Double price, String name) {
this.uuid = uuid;
this.price = price;
this.name = name;
}
public TestEntity() {
}
public String getUuid() {
return uuid;
}
public void setUuid(String uuid) {
this.uuid = uuid;
}
public Double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<Double, Double> function = (oo -> {
Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
return random.nextDouble() * 100 * oo;
});
List<TestEntity> entityList = new ArrayList<>();
entityList.add(new TestEntity(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), function.apply(100.01d), "a"));
entityList.add(new TestEntity(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), function.apply(199.01d), "a"));
entityList.add(new TestEntity(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), function.apply(97.01d), "b"));
Map<String, List<TestEntity>> listMap = entityList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(obj -> obj.getName()));
Map<String, Long> longMap = entityList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(obj -> obj.getName(), Collectors.counting()));
Map<String, DoubleSummaryStatistics> doubleSummaryStatisticsMap = entityList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(obj -> obj.getName(), Collectors.summarizingDouble(TestEntity::getPrice)));
doubleSummaryStatisticsMap.entrySet().stream().forEach(obj -> {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("最大值:" + obj.getValue().getMax());
stringBuilder.append("最小值:" + obj.getValue().getMin());
stringBuilder.append("合计值:" + obj.getValue().getSum());
stringBuilder.append("平均值:" + obj.getValue().getAverage());
stringBuilder.append("数量:" + obj.getValue().getCount());
System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
});
/*
最大值:14170.806808512518最小值:7121.362689911748合计值:21292.169498424264平均值:10646.084749212132数量:2
最大值:6907.74317116627最小值:6907.74317116627合计值:6907.74317116627平均值:6907.74317116627数量:1
* */
}
}
- Map&Reduce 收集器 (非常重要)
map将集合类(例如列表)元素进行转换的。还有一个 reduce() 函数可以将所有值合并成一个
package com.tool.stream;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Demo3 {
public static class TestEntity {
private String uuid;
private Double price;
private String name;
public String toString() {
return "TestEntity{" +
"uuid='" + uuid + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public TestEntity(String uuid, Double price, String name) {
this.uuid = uuid;
this.price = price;
this.name = name;
}
public TestEntity() {
}
public String getUuid() {
return uuid;
}
public void setUuid(String uuid) {
this.uuid = uuid;
}
public Double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<TestEntity> entityList = new ArrayList<>();
Function<Double, Double> function = (oo -> {
Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
return random.nextDouble() * 100 * oo;
});
entityList.add(new TestEntity(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), function.apply(100.01d), "a"));
entityList.add(new TestEntity(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), function.apply(199.01d), "a"));
entityList.add(new TestEntity(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), function.apply(97.01d), "b"));
entityList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy( obj -> obj.getName() ,Collectors.summarizingDouble(ooEntity -> ooEntity.getPrice()))).forEach((s, obj) -> {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("名称:").append(s).append(" ") ;
stringBuilder.append("最大值:" + obj.getMax());
stringBuilder.append("最小值:" + obj.getMin());
stringBuilder.append("合计值:" + obj.getSum());
stringBuilder.append("平均值:" + obj.getAverage());
stringBuilder.append("数量:" + obj.getCount());
System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(entityList.stream().map(obj -> obj.toString()).collect(Collectors.toList()).toArray())); ;
Double sumValue = entityList.stream().map(obj -> obj.getPrice()).reduce((sum, res) -> sum + res).get();
System.out.println("sumValue:"+sumValue);
}
}
- Collector 收集器 (非常重要)
七:自己总结的一些好用方法 #
- 去重
/**
* 去重
* 一个对象的去重例子 return list.stream().filter(StreamUtils.distinctByKey(o -> o.getId())).collect(Collectors.toList()); 如果不是id,是其它字段 同理 o.getId() 换为 o.getOther()
*
* @param keyExtractor
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
public static <T> Predicate<T> distinctByKey(Function<? super T, ?> keyExtractor) {
Map<Object, Boolean> seen = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
return t -> seen.putIfAbsent(keyExtractor.apply(t), Boolean.TRUE) == null;
}